The ESIGN Act and UETA Regulations Demystified p Even though a lot of the laws that pertain to electronic signatures have been covered, the topic of electronic signature regulations can still be compared to a labyrinth and a gray area that people can barely find the important path. But after you have become familiar with the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act and the National Electronic Signatures Act (UETA), you can conduct the business with legal matters in peace.
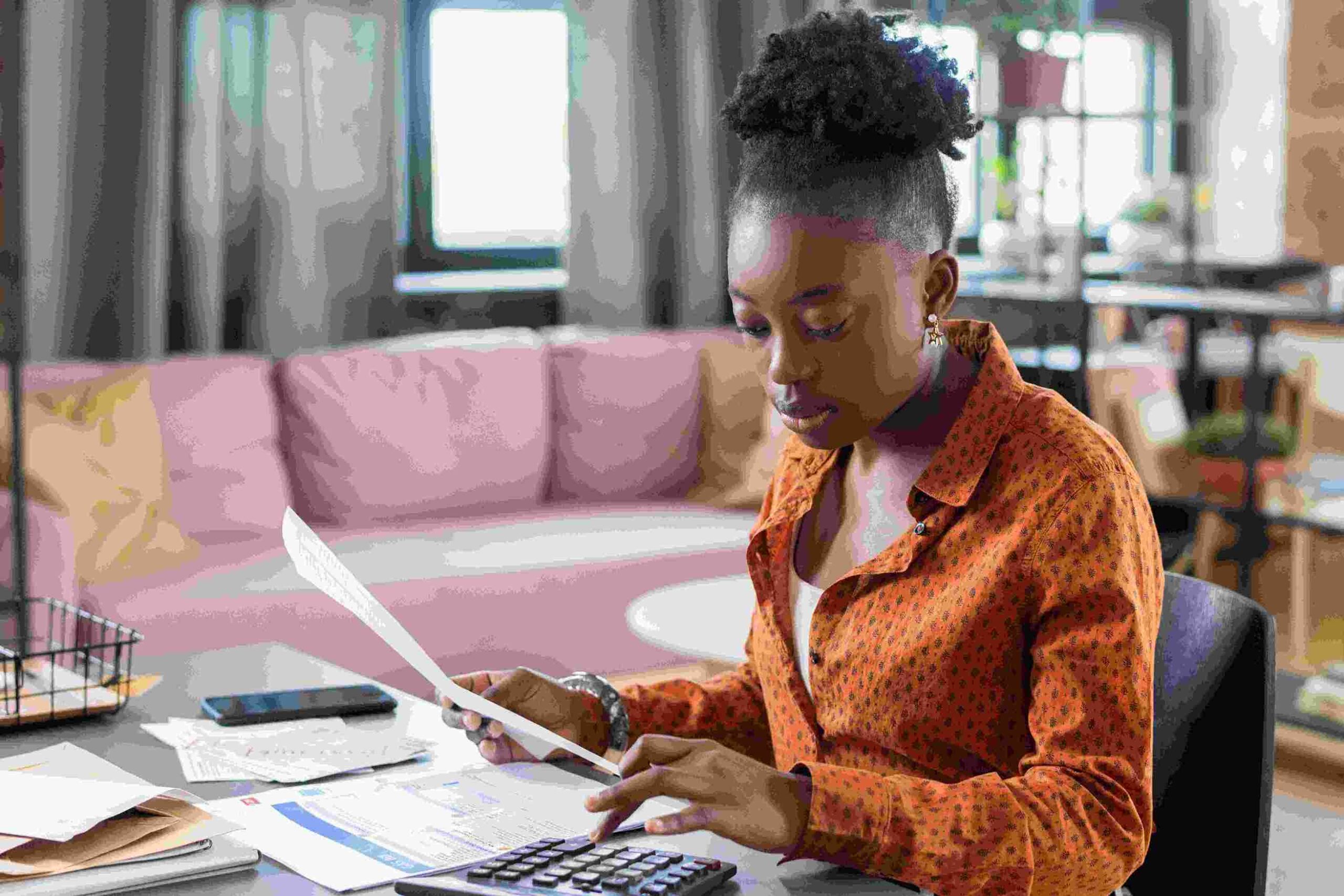
The conduct of business via electronic signatures has completely transformed the business world in an easy process and a hassle-free environment to sign a digital contract. The ESIGN Act, the implementation of which occurred when the Unites States Congress ratified it on the 30th of June, 2000, played an indispensable role in the whole affair. The delegation of power by the ESIGN Act for the legal use of electronic signatures in most transactions in interstate and foreign commerce has been a great step towards a business environment that is more efficient and transparent. The law through its provisions ensures that if the requirements are met, electronic signatures can be used and are as good as handwritten signatures. In this case, where the third parties are the users, they can safely give the form of a digital signature, and then the whole process will be very fast without any fear, that someone might tamper with the transaction, or that the transaction will be legally unjust.
The Influence of the ESIGN Act on the Way E-Signatures Are Accepted Electronic signatures can be used to sign the major part of the transactions in the US between the states and foreign commerce without any problems with the ESIGN Act. This rule covers particular circumstances that the electronic signature is as good as the handwritten one. Such a kind of formal allowance for both the business and the customers gives them the possibility to select the an electronic alternative to paper transactions which is favorable in all other aspects too.
Besides that, the Act has caused a lot of changes in quite a number of spheres, say, from finance to healthcare. The introduction of electronic signatures permits firms to automate their operations, reduce the consumption of paper, and at the same time to enhance the customer experience. The flexibility of action made possible by the ESIGN Act gives firms the power to go to the digital market space which in turn makes it achievable for them to cope with and also outcompete in the market can be said that ESIGN Act largely influenced a lot of fields, one of them being the financial industry. Simply put, the Act made it possible for the financial sector to adopt automation in their processing, decrease the amount of paper used, and, at the same time, have a more engaged customer base. Moving from the point of position the ESIGN Act is a federal act that enables states to allow the use of electronic signatures that are similar to hand-written signatures, it is also a federal act thus, the states are enabled to provide their regulations regarding electronic contracts that are uniform which are going to be a harmonized legal environment nationwide.
Having all electronic transactions defined in the same way around the country, UETA ensures that businesses operate under a predictable and consistent legal regime. In addition, by simplifying the process of the compliance requirements and promoting interstate commerce, UETA is also an advantage to those for enterprises which are multimodal and conduct business in various states. It is possible for businesses to perform secure electronic transactions across the different state jurisdictions through UETA, with the assurance that a uniform governance structure of the electronic signature usage at the state level is provided.
Entering the Marshes of US Electronic Signature Law Area
In general, the ESIGN Act and the UETA offer the basic framework for handling electronic signatures, while individual states’ laws further regulate the field. It is very important to be completely aware of such differences and requirements in each state where you have clients.
It could be that the variations in the Electronic signature laws in the different states are so drastic that the companies to have the tasks of ensuring the conformity. For instance, in some states, the laws are very strict as to what kind of transactions are allowed to be completed by the use of electronics but on the other hand, the e-signatures without the security measures can still be considered as valid.
Entitled New York’s Electronic Signature Legislation Unveiled
New York’s acknowledgment of electronic signatures is done through the New York Electronic Signatures and Records Act (ESRA), it sets to ensure that both the electronic signature itself and the electronic transactions executed are as admissible to the courts as those on paper. The Empire State not only invites the use of the electronic signature tool but also conforms itself to the digital environment, where people can now use digital resources for most of the activities.
According to the said law there are going to be lots of challenges and requirements in the New York market, and that ESRA is looking to avoid violations. By the companies taking their time to know and comply with the New York e-signature laws, they will be able to save time, eliminate all the red-tapes, and increase the efficiency of the business. The implementation of electronic signatures in New York not only gives companies the freedom to operate better but it is also an opportunity for them to improve customer service by offering their customers an easier way of doing things.
Debunking Electronic Signature Laws Misconceptions
One cannot deny that as electronic signatures become more prevalent among businesses there will also be plenty of questions and misinterpretations. Electronic signatures’ main issues usually concern the legality, acceptability, and multi-state usage of these electronic means.
What if we clarify all of those most common misunderstandings that we usually struggle with and then start to explore and describe the real situation?
Proving the Legal Validity of Electronic Signatures Across States
A question is often raised to the effect of whether the electronic signatures of different states are valid. Via the ESIGN Act, e-signature, which is a method where a person’s signature is recognized and, among other things, enforceable, is valid in all states. With the act, we are sure that the contracts made with e- signatures are legally valid and can be enforced even when the counterparty is in a different state where the law applies.
On the other hand, it is essential to remember that, notwithstanding the ESIGN Act as the federal source of reference for e-signatures, states have the privilege of adopting their rules, like the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA). These laws might be state-specific and thus setting up additional requirements or provisions that both companies and individuals need to be compliant with when making interstate transactions.
Understanding the Similarities and Differences between ESIGN and UETA
One of the questions frequently asked is the differences between the ESIGN Act and UETA. Both the ESIGN Act and the UETA laws are in consensus with electronic signatures as an acceptable way of signing. The ESIGN Act, however, has got the coverage at the national level, and thus, it sets the minimum requirements and standards for all the states to consider. On the contrary, the UETA Act which is a state-based law allows individual states to legislate according to their rules thus explains the differences in each and every state.
As an example, in the ESIGN Act, the definition of an electronic signature is “an electronic sound, symbol, or process attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.” On the other hand, UETA’s definition of an electronic signature is almost the same, but its use may be subject to further conditions, such as all parties’ consent or the use of certain technology.
Electronic Signatures and the Taxation Authority in the USA
One of the areas where the central government’s Internal Revenue Service has set the pace through the electronic recording and signing of tax returns is the highlighting of e-signatures and online systems. The BFSR notifies taxpayers as well that besides authorizing others to file on their behalf, they can also get their refund deposited directly into their bank accounts. A transition of this kind is not only time-saving, but it also encourages the individuals and companies to work efficiently.
Thus, to give an instance, the reader should keep in mind that not all IRS forms can be electronically signed. Otherwise, the IRS will not be able to process it. Correspondingly, the IRS can come up with a list of the form numbers that can be voted electronically. In addition to this, the taxpayers should also check online that they are opting for the right method for a certain form. Furthermore, tasks, for example, obtaining a Personal Identification Number (PIN) or adding some supplementary documents to the submission, may be required if one decides to e-sign the IRS document electronically.
By and large, e-signatures have demonstrated that they are the lifeblood of modern business trading that enables people to have the facility of doing penetrating their business with the traits of convenience, efficiency, and safety. Individuals and businesses who educate themselves about the laws and regulations of electronic signatures have become is able to lead the technological revolution more securely and depend among other things on this not just for digitization but also for business agility.
A Complete Explanation of the State-Specific Electronic Signature Regulations
Although we previously talked about the general legislation on electronic signatures, the main point that needs to be made is the individual regulations of each state. The ESIGN Act and UETA can be implemented all over the country, but there are some states that have additional requirements, which may be in this act, in other words, that can be found in it. Hence, users of electronic signatures have to take a look at the state-specific sources and get their signatures to be in compliance with the local regulations.
If we consider that California is the case, it contains several limitations of the UETA that could be used for electronic signatures. More specifically in California, the online signature is legally binding only when it’s a transaction carried out electronically and the both sides of the deal have decided on that issue. A contract can be executed in acts or may be written down in the contract as well. It’s essential for the business in California to be aware of these facts as it’s the only way for them to make sure that their electronic transactions are legal.
To give an example, the state of New York has Managed to pass their own Electronic Signatures and Records Act (ESRA) which sets the legal framework for the use of electronic signatures. ESRA establishes that the signing of documents electronically is both reliable and stored in the same way as in the customary way. Nevertheless, various documents like wills and trusts are subject to specific electronic signature conditions to be recognized as legally binding documents. Therefore, it is the obligation of commercial entities and citizens of New York to keep this law, as they would thereby mitigate the risk of legal problems that arise from electronic signatures.
What can BlueNotary do to help companies following state-specific electronic signature regulations in the best possible way?
BlueNotary can assist businesses in implementing state-specific electronic signature regulations by using a platform that is compliant with the ESIGN and UETA standards in full. This platform is equipped with such features as detailed logs and verification processes that not only make ES legal but also ensure the legality of electronic signatures. Additionally, BlueNotary provides a bunch of details not just to introduce but also to follow rules which are just for certain states like New York’s ESRA and California’s UETA provisions, hence allowing legal and efficient digital transactions across the states.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the exact fines and penalties to be paid because of the non-compliance of electronic signature laws?
A situation when someone fails to comply with electronic signature laws like ESIGN and UETA will result in electronic contracts that are not legally binding and, therefore, all parties can be sued for liabilities. In other words, different states would charge higher fines or expect imprisonment based on the weight of the violation.
Do electronic signature laws control the transactions between the U.S. and foreign countries involving electronic signature laws?
Only transactions made between the U.S. and its territories are the ones where electronic signature laws are effective like the ESIGN Act. To this end, the legality of electronic signatures in international transactions hinges upon the policies and rules of the countries involved. At the same time, U.S. companies are required to have the foreign country’s law on their side in adhering to the transaction to close legally.
What technologies or platforms have been recommended or certified for use under ESIGN and UETA?
It is important to note that the ESIGN and UETA Acts do not dictate specific technologies or platforms for electronic signatures but rather set a broad framework for any technology that meets certain requirements as to identity verification and record integrity. The companies should select only those technologies that have been confirmed to be with high-security levels by the industry and which are fully compliant.
Can the executive branch of the government use electronic signatures on other documents than IRS forms, for instance, passport applications, and social security documents?
Indeed, only a few government offices allow electronic signatures. Nevertheless, it is done on a case-by-case basis. For example, the U.S. State Department, at present, does not accept electronic signatures on passport applications owing to security reasons. However, other departments like the Social Security Administration may agree to electronic signatures for specific documents and services.
What is the technology behind these laws to prevent fraud?
The ESIGN and UETA laws lay down a rule that electronic signatures shall ensure the identification of the signers via digital certificates or biometric verification methods. This is a technological control that the sign in person masked the biggest share of fraud related to identity and, more ironically, only offered the opportunity to misuse a signature. Furthermore, the platform used to sign the document must have an inbuilt ability to track changes that might occur after the signature for it to remain a valid signed document.