Affidavit of Support Form Template
An Affidavit of Support Form is a crucial document used in immigration processes to demonstrate financial support for an immigrant by a sponsor. To access our Affidavit of Support Form Template, designed to assist sponsors in completing this important document accurately, click the button below. This template is essential for providing clear and comprehensive information required by immigration authorities.
Save time, avoid headaches, and ensure compliance effortlessly with current version of Affidavit of Support Form Template. With our streamlined process, you'll have your form in hand within moments, giving you the peace of mind to focus on what truly matters – your business.
Understanding the Template
How to Use the Template
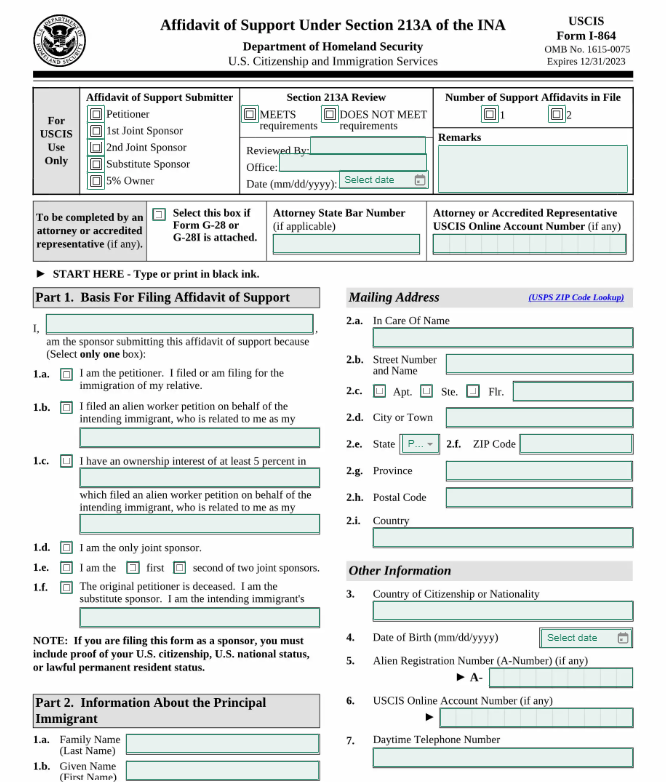
- Affiant Information: Provide information about the affiant (the person providing the affidavit of support), including full name, address, date of birth, and relationship to the immigrant.
- Immigrant Information: Provide information about the immigrant being sponsored, including full name, date of birth, country of birth, and relationship to the affiant.
- Financial Information: Disclose detailed financial information about the affiant, including income, assets, and liabilities. Attach supporting documents such as tax returns, bank statements, and employment verification.
- Household Size: Specify the total number of people living in the affiant's household, including dependents and other sponsored immigrants.
- Responsibilities of Sponsor: Acknowledge the responsibilities of the sponsor, including providing financial support to the immigrant and reimbursing the government for any means-tested public benefits received by the immigrant.
- Affidavit of Support Certification: Certify that the information provided in the affidavit of support is true and accurate to the best of the affiant's knowledge and belief.
- Signature and Notarization: Sign the affidavit of support in the presence of a notary public, who will verify the affiant's identity and witness the signature. The notary will also affix their seal and signature to the document.
Frequently Asked Questions
An Affidavit of Support Form is a document used in immigration processes to demonstrate financial support for an immigrant by a sponsor. It is required for certain visa applications, including family-based immigrant visas and some employment-based immigrant visas. The sponsor agrees to provide financial support to the immigrant and their dependents if necessary.
Sponsors who are financially supporting an immigrant's visa application should use an Affidavit of Support Form. This includes sponsors petitioning for family members, relatives, or fiancé(e)s to immigrate to the United States. The form is typically required as part of the visa application process to demonstrate the sponsor's ability to support the immigrant financially.
You can download the Affidavit of Support Form for free from reputable sources like our website BlueNotary or from immigration and visa application resources.


